March 29, 2021 ( last updated : March 29, 2021 )
이분탐색
그래프탐색
bfs
dfs
알고리즘
algorithm
https://github.com/sneakstarberry/
Abstract
[백준] 2585번 경비행기
[백준] 2585번 경비행기
알고리즘 유형
- 이분탐색
- 그래프탐색
- bfs
문제 이해
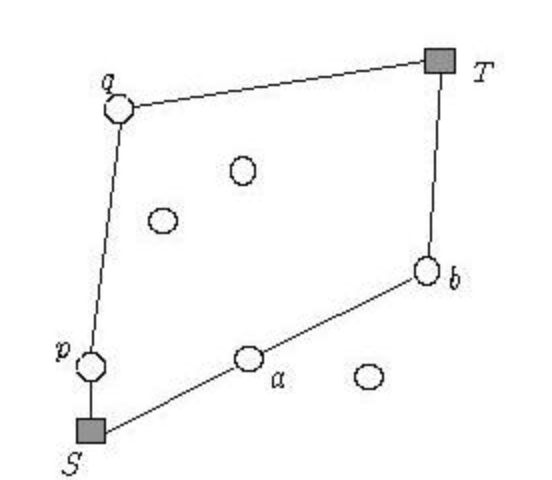 출발점(S) = {0,0}, 도착점(T) = {10000, 10000} 까지 가는 도중에 k번 이하 경유할 때 최소의 거리를 구하면 된다. k번 이하가 중요하다.
출발점(S) = {0,0}, 도착점(T) = {10000, 10000} 까지 가는 도중에 k번 이하 경유할 때 최소의 거리를 구하면 된다. k번 이하가 중요하다.
풀이방법
보자마자 문제는 이분탐색과 bfs 혹은 dfs를 써야한다는 것을 알았다. 비슷한 문제 유형을 많이 풀다보니 그냥 알게 된 것 같다. 하지만 이런 혼합형은 처음이었다.
여기서 알고 있던 것은 bfs로 탐색한 결과가 이분탐색에서 mid 값이 low가 될 것 인지 high가 될 것인지 결정하는 결과 겂이 될 것 이라는 것. 그리고 mid 값은 가장 적은 연료로 추정되는 값이라는 것 또한 알았다.
하지만 문제가 되는 것은 시작 점에서 도착점까지 거리를 측정하면서 갈 때 어떻게 k번을 맞추면서 가냐는 것이었다. 근데 k번 이하라서 상관없는 고민이었다. 오히려 k번 이하라는 조건이 다른 경우의 수를 거르는 거름망이 되었다.
풀이는 간단하다. 점을 bfs방식으로 방문하면서 매번 도착점까지 걸리는 연료의 값을 구해서 최소 연료 소모 추정값(mid)과 비교해서 가능한지 확인한다. 가능하면 high가 mid가 되고 불가능하면 low가 mid가 된다. k번 이하인지는 큐에 방문 노드 개수를 넣어두면된다. 해당 발상은 다른 bfs문제에서 해봐서 쉬웠다.
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, k, is_visited[1011];
double fuel(pair<int, int> _point1, pair<int, int> _point2);
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
pair<int, int> point[1011];
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> point[i].first >> point[i].second;
}
int l, h, m, minimum;
l = 0;
h = 20001;
minimum = 20001;
while (l + 1 < h) {
memset(is_visited, 0, sizeof(is_visited));
int reach = 0;
m = (h + l) / 2;
queue<pair<pair<int, int>, int>> q;
q.push({{0, 0}, 0});
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front().first.first;
int y = q.front().first.second;
int cnt = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if (cnt > k) {
reach = 0;
break;
}
if (fuel({10000, 10000}, {x, y}) <= m) {
reach = 1;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (is_visited[i])
continue;
int nx = point[i].first;
int ny = point[i].second;
if (fuel({nx, ny}, {x, y}) <= m) {
q.push({{ nx, ny}, cnt + 1});
is_visited[i] = 1;
}
}
}
if (reach) {
minimum = m;
h = m;
} else {
l = m;
}
}
cout << minimum;
}
double fuel(pair<int, int> _point1, pair<int, int> _point2) {
int _x = _point1.first - _point2.first;
int _y = _point1.second - _point2.second;
int _x_distance = _x * _x;
int _y_distance = _y * _y;
double _fuel = sqrt(_x_distance + _y_distance) / 10;
return _fuel;
}
Originally published March 29, 2021
Latest update March 29, 2021
Related posts :
- [백준] 15666 N과 M (12)
- [백준] 15663 N과 M (9)
- [백준] 15657 N과 M (8)
- [백준] 9251 LCS
- [백준] 2407 조합
- [백준] 13549 숨바꼭질 3
- [백준] 18119 단어 암기
- [백준] 13915 현수의 열기구 교실
- [백준] 11578 팀원 모집
- [백준] 1786 찾기
- [백준] 1701 Cubeditor
- [백준] 16916 부분 문자열
- [백준] 2003 수들의 합2
- [백준] 1806 부분합
- [백준] 1644 소수의 연속합
- [백준] 9661 돌게임7
- [백준] 9660 돌게임6
- [백준] 9659 돌게임5
- [백준] 9658 돌게임4
- [백준] 9657 돌게임3
- [백준] 9656 돌게임2
- [백준] 9655 돌게임
- [백준] 2042 구간 합 구하기
- [백준] 11505 구간 곱 구하기
- [백준] 10868 최솟값
- [백준] 2098 외판원 순회
- [백준] 15787 기차가 어둠을 헤치고 은하수를
- [백준] 1062 가르침
- [백준] 2022 사다리
- [백준] 9202 Boggle
- [백준] 2872 우리집엔 도서관이 있어
- [백준] 1927 최소 힙
- [백준] 11279 최대 힙
- [백준] 1325 효율적인 해킹
- [백준] 5052 전화번호 목록
- [백준] 2110 공유기 설치
- [백준] 1620 나는야 포켓몬 마스터 이다솜
- [백준] 1300 k번째 수
- [백준] 10816 숫자 카드2
- [백준] 10815번 숫자 카드
- [백준] 1219번 오민식의 고민
- [백준] 6359번 만취한 상범
- [백준] 2193번 이친수
- [백준] 2156번 포도주 시식
- [백준] 1912번 연속합